Michelle Has a High Level of Oxytocin in Her Body. This Helps Her ______ With Her Baby.
Abstract
Imagine that you want to tell your friends something new; you lot could whisper it into their ears or shout it out loud. This is rather like ii forms of communication that occur inside your brain. Your brain contains billions of nervus cells, chosen neurons, which make a very large number of connections with specialized parts of other neurons, called dendrites, to course networks. Neurons have been idea to communicate with each other by passing ("whispering") chemical signals directly through these connections, simply now we know that they as well can spread letters more widely ("public announcements") by releasing chemic signals from other parts of the neuron, including the dendrites themselves. If we sympathize how and what neurons communicate with each other, we will have a chance to correct disturbances in communication that may result in contradistinct behaviors and encephalon disorders.
We know that the human brain is the almost complex structure. It has approximately fourscore billion nerve cells, chosen neurons . Eighty billion (80,000,000,000)! This is more than than 10 times as many neurons as there are people living on World. Neurons talk to each other using special chemicals called neurotransmitters . Neurotransmitters are like chemical words, sending "messages" from one neuron to another. There are many different sorts of neurotransmitters: some stimulate neurons, making them more active; others inhibit them, making them less agile. Neurons control literally everything you exercise.
The Neurons are the Building Blocks of Your Brain
Neurons come in many forms, shapes and sizes, but it is helpful to retrieve of a neuron like a tree. A neuron has three master parts, the cell body, an axon, and the dendrites (Figure 1). The tree trunk (cell torso) stores genetic data (DNA) in a compartment chosen the nucleus. The cell body also contains the chemic machinery to produce the neurotransmitters that the neuron uses to communicate with each other.
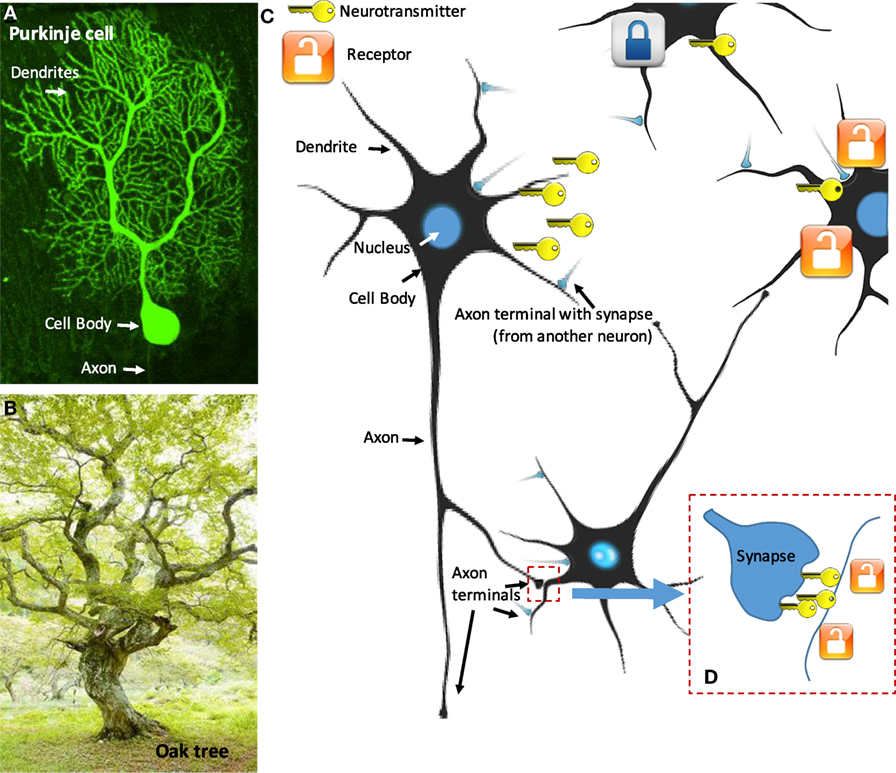
- Effigy 1
- A. Some neurons, like this special kind of neuron chosen a Purkinje jail cell, expect very similar to trees B. C. Neurotransmitters (cardinal) released from the axon terminals only accept to cantankerous a very tiny gap (a synapse) D. to reach their receptors (lock). However, when they are released from dendrites, their receptors tin can be far abroad and need to be reached by diffusion. Purkinje cell image courtesy of Marta Jelitai, Hungary.
The tree's branches (dendrite, the word déndron comes from the Greek language and really means "tree") are the parts of a neuron that receive signals. Dendrites were once thought to be like antennae, but receiving signals from other neurons, but, as I explain, they can practice more this.
The tree root (axon) is the structure used by a neuron to connect with and talk to another neuron. An axon carries information similar to a cable that carries electricity. When ane neuron wants to share a message with another, it sends an electric impulse, called an action potential, down its axon until it reaches the axon last, at the end of the axon. Think of an axon last as an airport last. An airport terminal is filled with passengers waiting to depart, whereas an axon final is filled with neurotransmitters waiting to travel to the adjacent neuron.
What are the Differences Between Wired and Wireless Transmission?
When the activity potential reaches the axon terminal, some of the neurotransmitters in the terminal are dumped into a tiny gap between the last and the dendrite of another neuron. This gap is called a synapse—it is so tiny that it is measured in nanometers or billionths of a meter. The neurotransmitter crosses the synapse and binds to a specialized site, called a receptor, on the other side. Each neurotransmitter binds only to its specific receptor, just as a fundamental fits only in a item lock. Depending on the neurotransmitter, information technology either stimulates the other neuron or inhibits, making it either more than probable or less likely to burn an action potential of its own. All these happens with very high precision and is repeated again and again. Since the signal is passed at very loftier speed from 1 neuron to another (upwardly to 100 one thousand/southward or 223 mph; faster than the fastest land mammal, the chetah, which can accelerate to a speed of 29 m/southward or 64 mph), this kind of communication betwixt neurons is sometimes called "wired transmission." The neurotransmitters pass "whispered secrets" direct from one neuron to another; they bear a bulletin that matters but at a item fourth dimension and identify. One style of thinking nigh "wired manual" is to think about a calorie-free switch, which switches a item light bulb on or off.
Some neurotransmitters, especially one kind chosen neuropeptides , are different. Neuropeptides are released from many parts of a neuron, including the dendrites. Rather than being released into the tiny synapse between an axon concluding and another neuron, they are released into the fluid that fills the spaces betwixt neurons, and they diffuse through the encephalon to attain receptors that are on distant targets. Ane manner of thinking near diffusion is to consider making your style through a wood (Effigy two). To get from 1 point to some other when no copse are effectually would be very simple and fast. One time you have a lot of copse, going from one point to another would take much longer fourth dimension, because you must get effectually the copse. So this sort of signaling is much slower than signaling at synapses, but eventually the neuropeptides will reach most parts of the brain. However, simply encephalon areas that have the correct receptors tin respond to the neuropeptides. So release of neuropeptides past dendrites, like Wi-Fi, is a wireless indicate—these messages are "public announcements" that are not sent from one prison cell to some other, merely from ane group of neurons to another group of neurons [one].
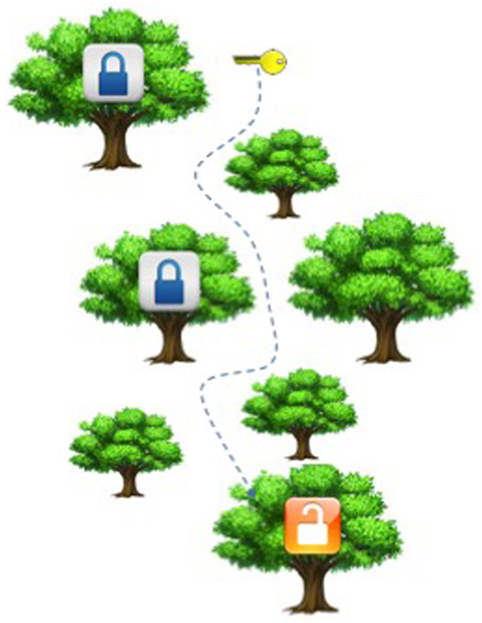
- Effigy two
- Neuropeptides (key) are released into the space between neurons (copse) and diffuse through the brain to reach receptors (locks) that can be on afar targets. Consider diffusion like making your mode through a forest. The time it takes to reach your lock (receptor) depends on how many copse (other neurons or cells) you accept to go effectually.
Oxytocin and Vasopressin Can Affect Behavior by "Wireless" Signaling
Let me utilise another example. The neuropeptides, oxytocin and vasopressin, are made by big neurons in the hypothalamus , a role of the brain that is important in regulating many physiological processes of the body. These big neurons accept ane axon that goes all the way to a specialized gland, the pituitary gland , which is attached to the bottom of the brain. From at that place, the neuropeptides are released from the axon terminals directly into the blood. Oxytocin travels through the torso and has a part in childbirth and breastfeeding. Vasopressin affects blood pressure and regulates the body's water balance through the kidneys. But both neuropeptides are as well released into the brain, where they control several sorts of behavior. For example, oxytocin helps a mother to bond with her child, and vasopressin affects retentiveness and aggression. Nevertheless, the brain areas that control these behaviors are sometimes far from the cells that make the neuropeptides. Some of these areas have the right receptors but no axons and terminals nearby, so that "wired" signaling by oxytocin and vasopressin cannot occur.
The oxytocin and vasopressin released from the axon terminals into the claret cannot re-enter the brain because of a strange structure called the claret–brain bulwark. Recollect nigh it, when y'all go sick, you do not want bacteria or viruses to invade your brain! The blood–brain barrier is a layer of cells keeping the encephalon safe from pathogens, toxins, and other molecules circulating in the blood. It prevents invaders from inbound the brain.
Yet, oxytocin and vasopressin are too released from the dendrites of the neurons, straight into the brain. Scientists have discovered that the release of neuropeptides from dendrites (into the encephalon) and from axons terminals (into the claret) can happen independently. Release of vasopressin and oxytocin from the axon terminals is controlled by activity potentials, like to the neurotransmitter release triggered in all other neurons. However, some chemical signals in the encephalon can stimulate neuropeptide release from the dendrites without triggering action potentials. Producing release in these different ways allows neuropeptide furnishings in the body and the brain to be regulated separately. For example, besides equally having effects on the body, such equally childbirth and breastfeeding, oxytocin besides stimulates the female parent'due south childcare and bonding—actions of the brain. This makes sure that the newborn receives all that is urgently needed: food and honey (Figure 3) [two].
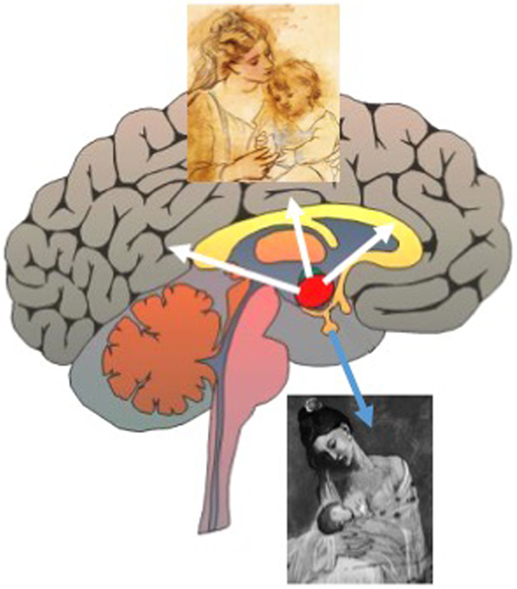
- Effigy 3
- Oxytocin is released into the blood from axons in the pituitary gland (blueish arrow) and into the brain (white arrows) from the dendrites of neurons in the hypothalamus (red area). Oxytocin acts both in the body and in the brain to make sure the child gets food (oxytocin's action on the body) and dear (oxytocin'due south activity on the encephalon).
Are Neuropeptides Similar to Hormones?
Release of neuropeptides past the dendrites of neurons is very similar to the release of hormones elsewhere in your body. Hormones are the chemical messengers released by glands and transported by the blood to afar target cells. So, hormones can stimulate cells that are located far abroad from the glands where they are produced. There are many unlike hormones, and they have lots of different functions in the body. For case, prolactin, some other hormone released from the pituitary gland, travels to a mother's breast where it stimulates the product of milk for breastfeeding. This procedure of "wireless signaling" by hormones is like the signaling by neuropeptides within the brain—so neuropeptides could exist called "brain hormones."
Why is it Important to Understand Neurotransmitter Signaling?
Some of the behavior disorders hardest to care for, for which new therapies are urgently needed, affect behaviors in which vasopressin and oxytocin are involved [three]. Every bit mentioned in a higher place, oxytocin is involved in childbirth, breastfeeding, and the mother'south behavior toward childcare. But oxytocin is besides of import for the child to develop and maintain complex interactions with others. Some children with autism oftentimes take difficulties in understanding and responding to those interactions, and scientists are trying oxytocin as a potential treatment (if you want to learn more than about this, read the article written past Daniel Quintana and Gail Alvares in the Frontiers for Immature Minds online library) [4].
Other examples include disorders associated with stress and anxiety, disorders of eating, disorders of substance misuse (including alcohol misuse), and disorders of sexual behavior. These are major health problems with a considerable impact on humans. By better agreement how brain cells and neuropeptides interact, we may find ways to control some of these disorders and meliorate the quality of our lives.
Glossary
Neuron: ↑ Cells of your nervous system, called nerve cells or neurons, are specialized to transmit "messages."
Neurotransmitters: ↑ Chemicals used by neurons to talk to each other—nosotros can call back of them every bit "chemical words."
Neuropeptides: ↑ A special type of neurotransmitter. They influence activities in the brain and body, for instance regulating a person's energy level.
Hypothalamus: ↑ The hypothalamus is a brain region that regulates functions like thirst, ambition, and slumber.
Pituitary Gland: ↑ The pituitary gland is located in a small-scale, bony cavity at the base of the brain. It is connected to the hypothalamus. It secretes hormones regulating many dissimilar bodily activities.
Hormones: ↑ Hormones are special chemicals that the body makes to assistance information technology do sure things like growing up and going through puberty, which is when y'all brainstorm developing into an adult. During this time, your body is loaded with hormones that tell it that it is fourth dimension to outset changing.
Autism: ↑ Many kids who have autism have trouble understanding what other people are thinking and how they are feeling. They might human action in a fashion that seems unusual, and information technology can be difficult to understand why they are acting that style.
Disharmonize of Interest Statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or fiscal relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
I would similar to thank my friends and colleagues at work who commented on the manuscript, especially my friends David and Gareth who made certain that I used the right words understandable for kids. I would as well like to thank Márta for the Purkinje jail cell image.
References
[1] ↑ Ludwig, Thousand., and Stern, J. Eastward. 2015. Multiple signalling modalities mediated past dendritic exocytosis of oxytocin and vasopressin. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 370(1672):20140182. doi:10.1098/rstb.2014.0182
[2] ↑ Ludwig, Grand., and Leng, G. 2006. Dendritic peptide release and peptide-dependent behaviours. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. seven:126–36. doi:10.1038/nrn1845
[three] ↑ Neumann, I. D., and Landgraf, R. 2012. Residual of encephalon oxytocin and vasopressin: implications for feet, depression, and social behaviors. Trends. Neurosci. 35:649–59. doi:ten.1016/j.tins.2012.08.004
[four] ↑ Quintana, D. S., and Alvares, G. A. 2016. Oxytocin: how does the neuropeptide change our social behaviours? Front. Young Minds iv:seven. doi:10.3389/frym.2016.00007
Source: https://kids.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frym.2017.00039
0 Response to "Michelle Has a High Level of Oxytocin in Her Body. This Helps Her ______ With Her Baby."
Post a Comment